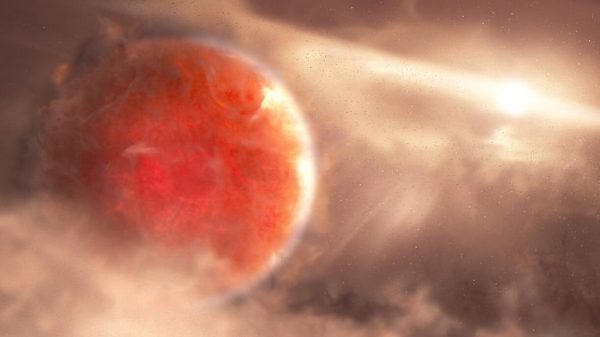
Astronomers have discovered the Milky Way’s “most massive” stellar black hole yet.
The newly discovered black hole is 33 times bigger than the sun and 2,000 light years away from us.
A stellar black hole is formed when a star collapses – and so far, the ones found in our galaxy have been about 10 times as big as the sun in terms of mass.
Scientists from the European Southern Observatory’s Gaia mission noticed the black hole after a star was spotted wobbling as it orbited the area. It has been named Gaia BH3.
“No one was expecting to find a high-mass black hole lurking nearby, undetected so far,” said Pasquale Panuzzo, an astronomer from the National Centre for Scientific Research at the Observatoire de Paris.
“This is the kind of discovery you make once in your research life.”
Important clues
Gaia BH3 is the second-closest black hole to Earth, sitting in the Aquila constellation, which means “the eagle” in Latin. From Earth, the constellation is thought to form the shape of an eagle.
The “wobbly” star orbiting it is thought to give important clues as to how the black hole was formed, as stars in pairs tend to be similar.
How are stellar black holes formed?
As stars reach the end of their lives, most of them inflate, lose mass and cool to form “white dwarfs”.
Stellar black holes are thought to form when a star doesn’t contain heavy elements and loses less mass over its lifetime – these are called “metal-poor” stars. Then, instead of changing and cooling into a white dwarf, it collapses in on itself and forms a black hole.
Gaia BH3’s companion star is a very metal-poor star which suggests that the star that collapsed to form BH3 was also metal-poor.
There are around 50 stellar black holes that scientists have discovered in the Milky Way, according to NASA.
In January, scientists discovered the oldest black hole ever, dating back to the early universe more than 13 billion years ago.
Spotted using the James Webb Space Telescope, that black hole is devouring an ancient galaxy called GN-z11 – 13.4 billion light years away. The universe is calculated to be 13.7 billion years old.